Morning music

On this day a year ago
Ukraine
The “hypocrite of the year” award must go to U.S. President Biden, on behalf of the American military and intelligence hierarchy, after Biden’s comment that Russian attacks on Ukrainian infrastructure were “brutal“: https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-europe-63208897.
It seems that semi-demented Biden has forgotten the US bombings of, inter alia, Afghanistan, Iraq, Libya, Serbia, North Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos, and North Korea, not to mention the annihilation of whole cities in the Second World War, mainly but not only in Japan and Germany.

The American governments of the past 80 years have killed untold millions.
Tweets about the Ukraine situation, seen overnight:
My view has been that the Russians fluffed what could and should have been a swift and unstoppable coup de main in February 2022. The Russian General Staff, GRU, and large parts of the Russian Army were shown to be incompetent, while their allies (Chechens mainly) were again proven to be brutal and out of control.
Also, the Russian side was unable to win or even seriously compete in the information and propaganda war. The “Ukrainian” (Jew-Zionist, mainly) side have had 8 months of uncritical support from the “Western” msm, even down to the extent that Kiev is no longer referred to as “Kiev” on “Western” TV or radio, but (e.g. on the BBC) as “Keev” (written version being “Kyiv“).
I had assumed that the Russian plan, once their absurdly half-hearted initial “invasion” stalled, would be to seize the Black Sea and Sea of Azov littoral as far inland as possible (which they have largely done, though stopping far short of the Odessa region), and to press up the eastern side of the Dnieper to some point southeast of Kiev, while also expanding west from Kharkov and advancing north from the Donbass, all three advances meeting southeast of Kiev, and so not only occupying most of eastern Ukraine but also laying the ground for a serious advance on Kiev from south, east and north.
If the above was the Russian plan, it now lies in tatters. The Kiev regime side, pumped up with Western weaponry and money, has advanced, and the Russian side withdrawn. The forces of the Kiev regime, having taken towns occupied previously by Russian forces, have executed civilians known to be pro-Russia and/or anti-war.
The recent attacks on the Nordstream2 pipeline and the Kerch Bridge (and an airfield in Kaluga region) betoken a serious escalation by the Western/NATO/NWO/Kiev side.
In the contemporary phrase, though, “we are where we are”. So where now?
We have just now seen Russian attacks mainly directed at electrical-generation and heating plants. These mark a change in strategy.
It seems that the Russian strategy as it now stands is to weaken the morale of the —so far largely untouched— populations in the large Ukrainian cities under control of the Kiev regime— Lvov, Odessa, Kharkov, and Kiev itself, among others.
I think that Putin was holding back from a really large-scale targeting of the Ukrainian population in order to leave the door open for negotiation, but the Jew Zelensky has recently made it clear that no negotiation will happen while Putin remains in place; also, that sovereignty over the Donbass, Crimea etc is non-negotiable. An “ultra” position, if you like.
That leaves only continuing war as a likelihood.
Winter is coming. Without heating or electricity, the living conditions of the Ukrainian civilian population may become dire. War is cruel, especially this type of attritional war.
The Zelensky regime continues to exist only by reason of the tens or hundreds of billions of US dollars (and devalued UK pounds) being funnelled to Zelensky’s apparat, together with advanced weaponry.
The Russian strategy is not so much one of weakening Ukraine economically. The Ukrainian economy is dead or dormant anyway. It is a question of sapping the civilian (and so also the military) morale until the moment is ripe to launch a killer blow, meaning either a larger-scale invasion directed mainly at Kiev, or the use of tactical nuclear weapons to literally blow Zelensky off his perch.
Positionally, the Belarus situation is interesting. Kiev is little more than 60 miles from the border with Belarus.
If the Russian forces can take Kiev at some point, the war will have reached a tipping-point both strategically and in terms of morale etc. The Zelensky regime will have been decapitated in terms of geography, and the Kiev-regime forces in eastern Ukraine cut off.
More music
Other tweets seen

Watch this space…
Truss and Kwarteng to destroy public services
Even for someone as cynical as I am about the UK’s totally broken pseudo-democratic system, the idea that the people of Britain can be put through such pain because a stupid woman who only became an MP in the first place on her back is “Prime Minister”, is unbelievable. Especially since said “ho” is only Prime Minister (in name) because 80,000 mostly elderly and comfortably-off Conservative Party members voted for her; even so, the vote was close. If Indian “clever boy” Sunak had not cheated the pensioners last year by suspending the “triple lock” on State Pensions, he would have clinched it.
As for Old Etonian woolly-head, Kwarteng, he takes the price of so-called “diversity” to a whole new level.
Short of a “grassy knoll” situation, how can this crazed dim woman and her cronies be removed?
I read that there are moves afoot to change the rules for removal of a Conservative Party leader, to shorten the 12-month time limit. That will take months, if it happens at all.
Alternatively, if Con Party MPs refuse to vote for Government measures, Truss might have to resign, but “have to” is not quite what it seems. She might simply dig in. I read her as the type of careerist, self-publicizing woman who will hang on as long as possible to the office, the pay, the perks, and the fact of being simply being the number one figure, even if powerless and widely despised.
One thing is for sure, the Conservative Party is toast from now on, unless it can find a semi-presentable leader by —at latest— Christmas 2023.
I think that abstention or protest voting will be more likely than a huge move by people to Labour. The huge opinion poll leads now being seen may persist, in our rigged binary system.
The UKIP debacle of 2015 (12% of votes but no seats) has put off many dissident conservative-“nationalist” voters, and the treachery of Farage in 2019 re. his Brexit Party has surely finished off that “Conservative Plus Plus” populism, at least in any significant way.
As we know, what matters, usually, is what happens in a few dozen very marginal seats. That is where the Conservative Party’s main weakness lies. Seats such as those former “Red Wall” constituencies “up North”.
I am sure that the old “Red Wall” can never be put back together, by reason of societal changes. Instead of the “proletariat”— miners, dockers, railway workers, steelworkers— you have call centre workers, retail workers etc, the “precariat”. Volatile voters, who might vote Labour one year, Conservative the next, and (?) UKIP, Brexit Party (or whatever) the year after that.
Still, the former “Red Wall”, which voted Con in 2019, will probably swing back to Labour, if only in the short term, meaning in 2023/2024. That alone is enough to cook the Conservative goose.
If the Conservative Party continues at 20%-25% in the polls, then it will not win any marginal seats, and will almost certainly lose seats not usually marginal.
Much depends on what happens to people’s lifestyles between now and the end of 2024, the last time when a general election can be held. If the Conservative MPs cannot hold the Truss feet to the fire in a major way, Conservative Party support may “trickle down” the drain even further…
Sadly, there is no social national party to engage with the people. The little joke-parties, such as For Britain and Britain First, have disappeared from view, and recent by-elections have been embarrassing for the few sort-of social-national candidates (eg Jayda Fransen) who have tried to put themselves forward. Indeed, the mere fact that I have even bothered to mention Jayda Fransen etc shows how empty the social-national space is in the UK.
“Just Stop Oil” nonsense
Stupid smug idiots who should get kicked in the head.
See also: https://ianrobertmillard.org/2019/09/29/greta-thunberg-system-approved-wunderkind/; and https://ianrmillard.wordpress.com/2019/08/16/the-extinction-rebellion-levellers/; and https://ianrobertmillard.org/2019/10/09/extinction-rebellion-greta-thunberg-cressida-dick-and-the-madness-of-protesting-crowds/; and https://ianrobertmillard.org/2020/09/08/diary-blog-8-september-2020-including-further-assessment-of-extinction-rebellion-as-well-as-of-tim-crosland-and-plan-b-etc/.
Not that I oppose genuine environmentalism, which has always been linked to social nationalism: https://ianrmillard.wordpress.com/2016/11/17/social-nationalism-and-green-politics/
More tweets
That is my view too. If the Scottish people want to be nominally “independent” (if that means anything when Scotland would still be part of NATO, a reconnected EU, and the international banking system), then fine, just go (and with my genuine blessings), but in that event Scotland will almost certainly have to accept far lower living standards. Fact.
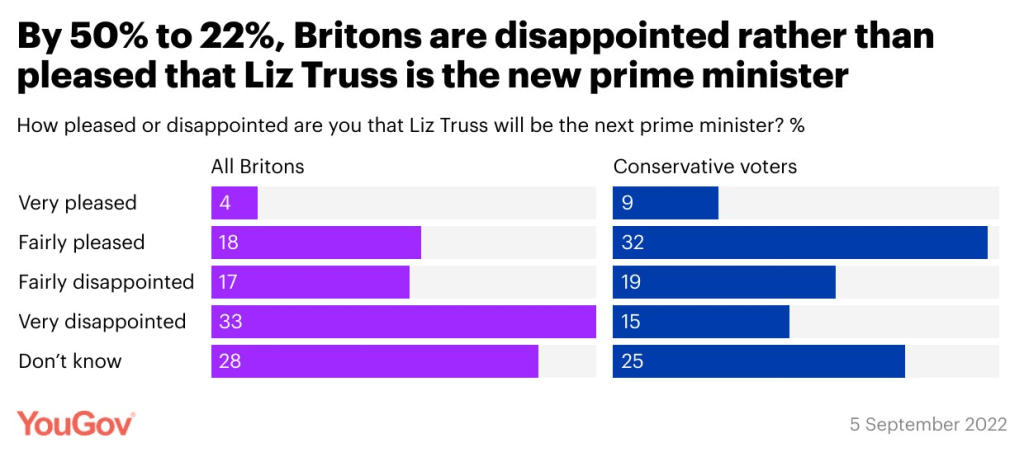
In fact, it seems to be that many Scots want, not “independence” but simply greater autonomy, meaning freedom from Westminster. See, below, the latest YouGov poll re. retaining the Monarchy:
Evenly divided. In a sense, that poll surprises me; I should have expected at least a small majority to be hostile to the idea of retaining the Monarchy.
SNP support is still at or below 50%:
That probably puts support for “independence” even lower, maybe (at an educated guess) around 45%.
An even more “autonomous” Scotland than exists at present would probably reduce the pro-Independence figure lower still.
If Scotland has even more autonomy, though, it cannot expect to retain funding on an overly-generous scale from the UK as a whole.
More tweets
Horrible. See also: https://ianrobertmillard.org/2018/12/10/tv-ads-and-soaps-are-the-propaganda-preferred-by-the-system-in-the-uk/.
You can easily guess which (((element))) is behind much of it.
Piers Morgan might be called just an idiot (after all, he is an uneducated and uncultured man— https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Piers_Morgan), but at the same time he is a chosen —or should that be “chosen by the (((chosen)))”— System mouthpiece on the msm.
People such as Morgan are pushing the idea that “Ukraine” (Kiev regime) can “win” this war. How? By NATO etc giving Zelensky long-range weapons with which to hit Moscow and Petersburg? Does Morgan himself really believe that Russia will just sit still if Kiev-regime forces capture all of the Donbass (and also Crimea, where 95% of the population is Russian)? The slaughter and terror likely to be inflicted on the Russian and also pro-Russian Ukrainian populations by the Kiev regime would be terrible.
Strange, I did not see or hear Morgan oppose the large-scale bombings (and huge civilian casualties) in Afghanistan and Iraq by American and UK forces. Maybe not so strange— Morgan’s brother is or was an Army officer of field rank, who served in at least one of those theatres; possibly both.
Reverting to the idea that Ukraine can “win”, what would that look like?
Let us say that Russia withdraws all forces from Crimea (Russian territory since the time of Peter the Great —and before then Tatar/Turkic— with the exception of the decades since 1953);
Let us say that Russia withdraws from the Donbass etc. What then?
Then Ukraine (Kiev regime) would be built up by NATO with huge new weapons influxes, possibly even tactical nuclear. Russia would be forced to agree “reparations” with Kiev (with NATO standing behind) and, down the line, Russia would be forced into a position of subservience to (((Western))) interests even worse than happened under Yeltsin in the 1990s. Russia was on its knees then. I saw it myself.
The more I look at it, the more I think it quite likely that Russia and the Western powers (NWO) will eventually end up in a strategic nuclear exchange that will change all of our lives irretrievably. If so, a large part of the blame and guilt will rest with a warmongering Western msm; people such as Piers Morgan. He may eventually reflect on that, if it happens and if he survives.
I see from his Wikipedia entry that Morgan has his main base not in the UK but in Los Angeles, though he has properties in both London and Sussex as well; maybe elsewhere too.
Late music